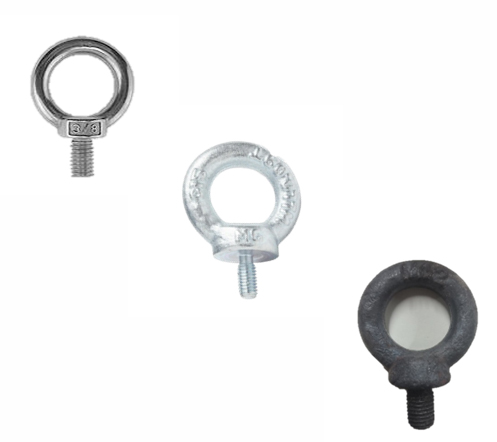
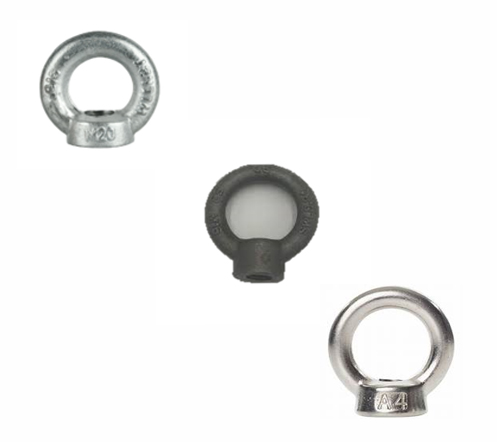
Key features of an eye bolt
include:
1.Threaded Shank:
The shank of the eye bolt is
threaded, allowing it to be screwed
into various materials, such as
wood,
metal, or concrete, depending on the
type of eye bolt and the intended
application.
2.Eye or Eyelet:
The circular or oval loop at one end
of the eye bolt provides a means of
attaching cables, ropes, or other
components. The size and shape of
the eye can vary, depending on the
eye bolt's design and load capacity.
Eye bolts come in various types
and configurations, including:
1.Shoulder Eye
Bolt:
These eye bolts have a shoulder or
collar below the eye. The shoulder
provides additional support to
prevent the eye bolt from embedding
too deeply into the material.
2.Lag Eye Bolt:
Lag eye bolts are designed for
attachment to wood, with a threaded
portion that is partially or fully
embedded in the wood, and an eye for
securing ropes or cables.
3.Screw Eye Bolt:
Screw eye bolts have a threaded shank
that can be screwed into various
materials and are commonly
used for hanging or suspending
items.
4.Machine Eye
Bolt:
Machine eye bolts have a fully
threaded shank and are typically
used in machinery and other
industrial
applications.
5.Concrete Eye
Bolt:
These eye bolts are specifically
designed for use in concrete, with
anchors that provide secure
attachment to concrete structures.
Eye bolts are used in a wide
range of applications, such as:
Lifting and rigging operations.
Securing loads in construction and
manufacturing.
Hanging objects, decorations, or
signs.
Boat rigging and maritime
applications.
Creating anchor points for safety
harnesses and fall protection
systems.
When using eye bolts, it is crucial
to ensure that they are properly
rated for the intended load and
application. They should
be installed according to the
manufacturer's recommendations and
inspected regularly for wear and
damage to maintain
safety and reliability. The eye bolt
and its attachment should be
inspected to ensure that they meet
safety standards and
regulations, particularly in lifting
and load-bearing applications.